Semantic search and its application

“Semantic search is Google’s growing ability to make associations between things in ways that come closer to how we humans make such connections.” – Mark Traphagen, of Stone Temple
What Does Semantic Search Mean?
Semantic search is a data searching technique in which a search query aims to not only find keywords but to determine the intent and contextual meaning of the words a person is using for a search. It uses vector search and machine learning to return results that aim to match a user’s query, even when there are no word matches. To best find and rank results, the semantic search will compare thousands of different properties that have been learned by machine learning and come back with a number that specifies how similar a record is to a query based on a formula that it has, again, derived through machine learning.
Now, you may be asking in your mind, It’s complex? yes, and powerful.
According to Wikipedia, it seeks to improve search accuracy by understanding the searcher's intent and the contextual meaning of terms as they appear in the searchable dataspace, whether on the Web or within a closed system, to generate more relevant results. Content that ranks well in semantic search is well-written in a natural voice, focuses on the user's intent, and considers related topics that the user may look for in the future.
Semantic search is used strategically by companies for knowledge management. It allows for meaningful and seamless data-sharing by employees across teams and locations based on contextual references. Even social media companies employ it on their platforms to help users explore common interests, trending topics, and products and services advertised by different businesses and organizations.
Let's use Google search as an example, when the user searches for just a single keyword like burger they will provide with location to order burgers, which seems that Google the majority of people searching for burger are interested in ordering burgers. Along with creating links between the words in the query, this personalizes the search to make the experience relevant to your user.
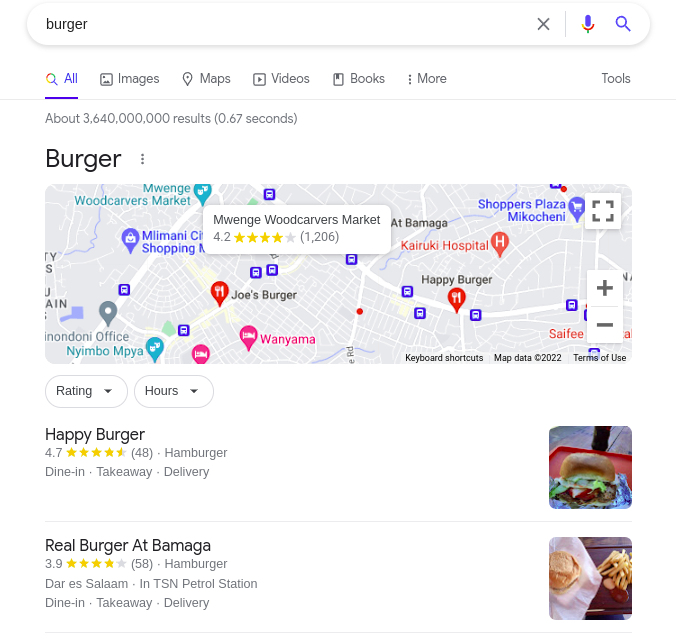
But, when it comes to a long query the results will be based on the intent and contextual meaning of the query.
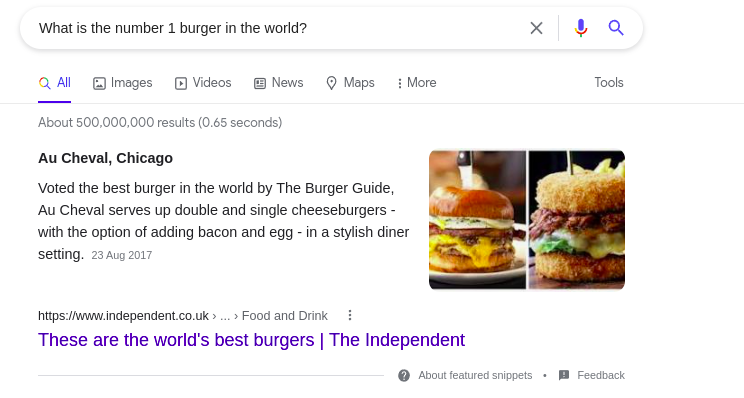
How Does Semantic Search Work?
The Semantic Search algorithm works by discovering contextual relationships between words and terms. Through natural language processing techniques like named entity recognition (NER), the algorithm recognizes and extracts entities in a text. When a person inputs a query into a search engine like Google, Bing, or a company’s private intelligent search engine, the NLP algorithms break down the query into subsets. They use tasks such as error correction, synonyms, POS tagging retrieval, and conversion to word embeddings to analyze the text. Combining all these activities, they extract relevant details from the data source and present the user with precise results.
By integrating NER with the semantic search you achieve better contextual meaningful insights from customer words. This provides an understanding of the intent of your customer and identifies the key themes, topics, and ideas that your customers are talking about on social media, surveys, and any other text that's important to your organization. This can help in adjusting business strategies to better fit the customer's needs.
Is semantic search applicable in your business and marketing plans, and how can you use it to your advantage?

Keep in mind that Semantic searches don’t match on text, but on the meaning.
Applications of Semantic Search
Let's look at how Semantic search can be applicable in different fields
- In information categorization: as companies around the world strive to find better options for managing the flow of unstructured information, they often turn to the classification systems, Semantic search tools can be applied in categorizing information to fit the intent and the contextual meaning of the information into specific categories.
- In Research: Most of the research companies need the Semantic search for essential analysis of information from several sources. Semantic search plays a great role in understanding the potential area and techniques over other competitors.
- Extracting metadata from images, the image search engine allows for the search of patent material with images similar to images or features provided by the user. The objective of the multimodal search is to improve the performance of the classical retrieval techniques with the inclusion of the results from the advanced search methodologies. Semantic search can help in extracting a set of data describing and providing information about the rights and administration of an image.
- Enterprise Knowledge Management: Organizations use Semantic search in understanding various vital needs for knowledge management across areas like customer voice data, employee data, customer feedback, etc From tasks like search and retrieval to sentiment analysis of reviews and comments, semantic search solutions enable enterprise teams to access organization-wide information seamlessly and integrate business intelligence strategies.
- Indexing the company's information, in cleaning and slicing documents into meaningful sections, then the meaning of each section is numerically encoded as a semantic fingerprint, An inverted index of section fingerprints is created and finally, you can easily add, change, or delete document sections in the index. You can read more about this application here.
- Searching for pieces of information, able to enter a search query that consists of words, semantic expressions, text, or sample documents in a search engine like Google, Bing, or a company’s private intelligent search engine, where the results are ranked based on semantic similarity. This is commonly one simply because you struggle with browser pages every day looking for different pieces of information or even fixing program errors for developers.
- In Smart Devices: Devices like Smart cars, laptops, smartphones, Smartwatches, and digital appliances all use semantic search technologies. let me use a simple scenario when your phone understands an incorrect spelling and gives you the right answer, when your smart device remembers your favorite song. All of these are using intelligent algorithms that understand your query through contextual reference.
- Spelling Tolerance: In different search applications ranging from intranet search engines, job portals for engineers, search engines for jobs, and continued education for workers, found that the users made a lot of typing and spelling errors. While simple errors like inclusion, omission, exchange, and permutation of characters are quite easy to identify and in simple cases can be automatically corrected.
- In Marketing: Semantic Search was one of the key elements that created this new customer experience era. Now is most of the time your focus should be on making their experience - online and offline - as simple and as beneficial to them as possible. Businesses such as digital marketing, non-profit, and eCommerce are shifting towards a place where it is the customer who has the power. All of these are the result of features like personalization and suggestion-based browsing of the incredible access to a widespread amount of information.
- News Monitoring: companies use semantic search in monitoring their news to keep track of their brand reputation, competitor analysis, and other affairs that affect their markets. News monitoring may vary across industries but the semantic search can be applied in analysis of information of various use-cases depending on company goals.
A semantic search is better because trying to provide a more accurate result, compared to other traditional search techniques. If search engines were merely returning results based on keywords, you wouldn't like the search results you were getting. The very best results can only be returned by taking into consideration the semantic factors of the information.

